The journey to becoming a licensed architect in Virginia encompasses a thorough educational background, practical experience, and passing a series of examinations. This article delves into the specifics of each step, offering insights into the requirements set by the Virginia Board for Architects and the value of obtaining this prestigious certification.
By understanding the nuances of the process and the benefits it brings, aspiring architects can navigate their path to success with clarity and confidence.
Comprehensive Path to Virginia Architect Licensure
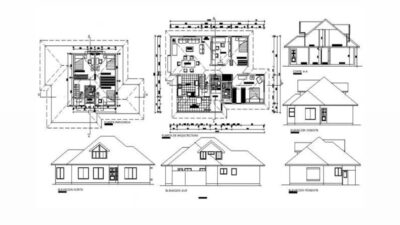
Obtaining an architect’s licensure in Virginia begins with formal education. Candidates must graduate from a program accredited by the National Architectural Accrediting Board (NAAB). Options include a five-year Bachelor of Architecture (B.Arch) program or a two-year Master of Architecture (M.Arch) program. These comprehensive courses cover a range of subjects from design theory to technical aspects of construction.
The next phase involves gaining practical experience, which is crucial for hands-on learning and the application of theoretical knowledge. The Virginia Board for Architects requires a minimum of three years of professional experience under the guidance of a licensed architect. This period is instrumental in developing a deeper understanding of architectural practices and client interactions.
Navigating the Architect Registration Examination (ARE)
Successful completion of the Architect Registration Examination (ARE) is a critical step. Administered by the National Council of Architectural Registration Boards (NCARB), this examination tests knowledge and skills in key areas such as:
- Site Planning;
- Building Systems;
- Construction Documentation.
The ARE is divided into six sections, each focusing on a different aspect of architecture. Candidates must pass all divisions within five years to qualify for licensure in Virginia.
Application and Licensure
To apply for a PE license in Virginia, candidates must:
- Meet general standards and requirements set by the state board;
- Successfully clear all steps, including the PE exam;
- Await the board’s processing of their application and issuance of the license.
Key aspects include:
- Payment of application and exam processing fees;
- Adherence to the board’s timelines.
Why Pursue a Professional Engineer License?
A professional engineer (PE) license marks a significant milestone in an engineer’s career. It opens doors to advanced career opportunities, such as:
- Senior engineering positions;
- Advertising engineering services;
- Involvement in public safety and patent work;
- Expert witness testimony.
Licensed PEs often enjoy higher compensation and are regarded with greater professional respect.
General Application Requirements for a PE License in Virginia
To apply for a PE license in Virginia, applicants must adhere to specific requirements:
- Demonstrating good moral character;
- Timely and accurate completion of the application as per board instructions;
- Submission of required test results before the board’s deadline;
- Submission of all documents and fees within three years of the initial application date;
- Undergoing additional board examinations and inquiries for document and qualification verification;
- Providing requested additional documents or information within 60 days of notification;
- Potential acceptance of applicants not meeting requirements, based on the Virginia Administrative Process Act provisions.
Maintaining Architect Licensure
Architects in Virginia must fulfill continuing education requirements to maintain their licensure. This involves:
- Completing approved coursework every two years;
- Staying informed about industry developments and innovations.
These requirements ensure that architects remain knowledgeable and capable in their field.
Requirements for Architect Licensure
Architect license candidates in Virginia must:
- Hold a bachelor’s degree or higher in architecture;
- Submit a degree verification form;
- Provide three professional reference letters or a certificate record;
- Achieve passing scores on all portions of the Architect Registration Exam;
- Renew licenses every two years, including completing 16 hours of continuing education and paying a renewal fee.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Licensed architects in Virginia must possess a diverse skill set, including:
- Proficiency in architectural design and understanding of construction materials and techniques;
- Mastery of computer-aided design (CAD) software for creating detailed plans and models;
- Knowledge of building codes, regulations, zoning laws, and environmental considerations;
- Effective communication skills for liaising with clients, contractors, and stakeholders;
- Strong project management abilities to oversee budgets, timelines, and team coordination.
These competencies ensure architects can deliver high-quality, compliant, and innovative designs.
Local Salary Expectations for Licensed Architects
In Virginia, licensed architects can anticipate a financially rewarding career. The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports a median annual wage for architects in the region at approximately $84,470. However, several factors influence this figure:
- Experience Level: More seasoned architects typically command higher salaries due to their extensive expertise and track record in the field;
- Firm Size: Larger architectural firms often offer higher compensation compared to smaller practices, reflecting the scale and complexity of projects they handle;
- Geographical Location: Urban centers like Richmond and Virginia Beach generally offer higher salaries compared to rural areas, owing to the higher cost of living and concentration of large-scale projects;
- Specialization and Certifications: Architects with niche skills or additional certifications may be eligible for increased pay, recognizing their specialized expertise.
These factors collectively contribute to the earning potential of architects in Virginia, making it a lucrative and stable career path.
The Impact of Technological Advancements on Architecture
The field of architecture in Virginia is continually evolving, significantly influenced by technological advancements. These changes not only streamline design processes but also open new avenues for creativity and innovation:
- Integration of BIM (Building Information Modeling): This technology revolutionizes design and construction, enabling architects to create more accurate, detailed models of buildings;
- Use of Advanced CAD Software: The adoption of sophisticated computer-aided design software allows for more precise and intricate designs, enhancing the quality and efficiency of architectural work;
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): These technologies offer immersive experiences, helping clients visualize projects in a more tangible way before construction begins;
- Sustainable Design Technologies: With a growing emphasis on sustainability, architects are increasingly using tools that help design energy-efficient and environmentally friendly structures.
These technological trends not only enhance the efficiency and quality of architectural designs but also broaden the scope of what is possible in the field.
Preparing for Architectural Trends and Changes
Staying abreast of emerging trends and changes is crucial for architects in Virginia. This foresight ensures that professionals remain relevant and competitive in an ever-evolving industry. Key areas to focus on include:
- Sustainable and Green Building Practices: With a growing emphasis on environmental conservation, knowledge of eco-friendly design principles is becoming indispensable;
- Adaptation to New Building Materials and Techniques: Innovations in materials and construction methods demand continual learning and adaptation;
- Understanding of Zoning Laws and Regulations Updates: Staying informed about changes in building codes and zoning regulations is critical for compliance and successful project execution.
For architects aspiring to expand their practice beyond Virginia, it’s beneficial to explore licensure requirements in other states, such as Massachusetts, where architectural standards and industry dynamics may differ.
Conclusion
From the foundational steps of obtaining a license to understanding local salary expectations and the impact of technological advancements, this article has covered the comprehensive journey of becoming a licensed architect in Virginia. The path involves rigorous education, practical experience, passing the ARE, and staying informed about industry trends and technological innovations.
Architects in Virginia are well-positioned to embark on a financially rewarding and professionally fulfilling career, equipped with the knowledge to navigate the dynamic landscape of modern architecture. Moreover, the insights provided extend beyond the state’s borders, preparing professionals for opportunities in other regions, like Massachusetts, where architectural practices continue to evolve.